Table of Contents
ToggleV8 Cars: Engineering Excellence and the Soul of Performance

The automotive world has been shaped by many powerful innovations, but few have defined driving enthusiasm and performance like the V8 engine. Known for its unique growl, balanced power delivery, and versatility, the V8 engine has been the heart of performance vehicles, muscle cars, and luxury sedans for over a century. Despite evolving trends and tightening environmental regulations, the V8 continues to command respect and admiration among automotive enthusiasts.
In this article, we will explore the origins, design principles, impact, and future of V8 cars, highlighting why they have become a symbol of automotive passion.
The Origins of the V8 Engine V8 Cars
1.1 Early Development
The V8 engine configuration dates back to the early 1900s. The first known V8 engine was designed by French engineer Léon Levavasseur in 1904, initially used in speedboats and aircraft. Its compact size and power potential made it a promising layout for internal combustion.
In the automotive realm, the V8 started to appear in luxury and performance cars in the 1910s. Cadillac is often credited with producing the first mass-market V8 engine in 1914. This set the stage for the V8 to become a staple in American engineering.
1.2 Mass Production and American Dominance
By the 1930s, Ford revolutionized the market with its flathead V8, offering affordable power to the masses. This engine played a pivotal role in democratizing performance and laid the foundation for the American love affair with V8 cars.
Engineering and Design
2.1 What is a V8 Engine?
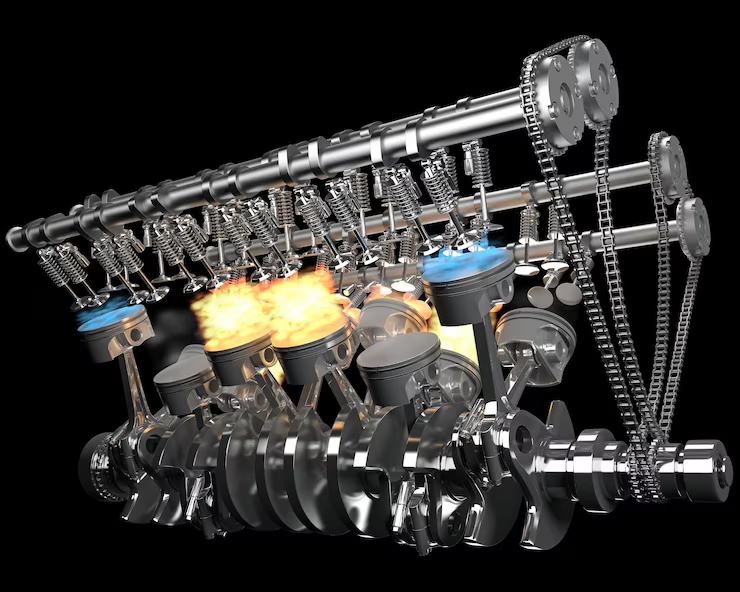
A V8 engine has eight cylinders arranged in two banks of four, forming a “V” shape. These banks are typically placed at a 90-degree angle, although variations exist. Each cylinder has a piston that moves to create power through combustion, and the engine’s crankshaft converts this motion into rotational force.
2.2 Performance Benefits
-
Balance: V8 engines are well-balanced, reducing vibration and increasing smoothness.
-
Power-to-Size Ratio: The layout allows more power in a relatively compact space.
-
Torque Delivery: V8s offer excellent low-end torque, ideal for towing and acceleration.
-
Sound and Feel: The rumble of a V8 is distinctive, often described as visceral and exciting.
Iconic V8 Cars Throughout History V8 Cars

3.1 American Muscle Cars
The 1960s and 1970s are often referred to as the golden age of V8s in the U.S. This era gave birth to the muscle car movement:
-
Ford Mustang GT – A cultural icon with its V8-powered variants.
-
Chevrolet Camaro SS—A direct rival to the Mustang, powered by small-block and big-block V8s.
-
Dodge Charger R/T – Known for its V8 engine and menacing presence.
3.2 European Engineering Meets V8 Power
While Europeans favored smaller engines, they embraced the V8 for luxury and performance models:
-
Ferrari 308 GTB – Combined mid-engine dynamics with a compact V8.
-
BMW M5 (E39) – The 4.9L V8 in this car became a benchmark for performance sedans.
-
Mercedes-Benz AMG models – AMG’s hand-built V8s were known for power and precision.
3.3 Japanese Contributions
Japanese automakers have also embraced V8s, particularly in their luxury divisions:
-
Lexus LS400 – Debuted with a smooth, quiet 4.0L V8 that rivaled German luxury sedans.
-
Nissan Titan & Infiniti QX56 – Used V8s for both workhorse and luxury SUV applications.
Cultural Significance V8 Cars
4.1 The Soundtrack of Freedom
In the U.S., the V8 engine is more than just mechanical—it represents freedom, rebellion, and power. The sound of a throaty V8 rumbling down the highway has become synonymous with American car culture.
4.2 Film and Media
V8 cars have starred in countless films and TV shows:
-
“Bullitt” – The Ford Mustang GT390’s chase scene became legendary.
-
“Mad Max” – The Interceptor, powered by a V8, symbolized post-apocalyptic power.
-
“Fast & Furious” – Many muscle cars in the franchise sport high-displacement V8s.
4.3 Motorsports Legacy
V8 engines have been integral to motorsports:
-
NASCAR – Exclusively uses V8 engines, pushing them to high limits.
-
Formula 1 – Used naturally aspirated V8s from 2006 to 2013.
-
V8 Supercars (Australia) – A series named after the engine itself, showcasing high-speed touring cars.
Advantages of V8 Cars
5.1 Power and Performance
The primary benefit is sheer power. V8 cars deliver high horsepower and torque, making them ideal for performance enthusiasts and professional applications like towing or racing.
5.2 Durability
Many V8 engines are known for their robust construction and longevity. They often have stronger internals than smaller engines to handle increased power, contributing to their durability.
5.3 Versatility
Whether in a muscle car, luxury sedan, or pickup truck, the V8 can adapt to a wide range of uses.
Challenges and Downsides V8 Cars
6.1 Fuel Consumption
V8 engines typically consume more fuel than four- or six-cylinder engines. This becomes a significant disadvantage with rising fuel prices and stricter fuel economy standards.
6.2 Environmental Impact
Higher emissions are a concern. Regulatory bodies worldwide are enforcing tighter emission standards, which affect the viability of large, naturally aspirated engines.
6.3 Cost
V8 cars are generally more expensive due to larger engines and the engineering required to handle the power. Maintenance and insurance costs can also be higher.
The Evolution of the V8 Cars
7.1 Downsizing and Turbocharging
To address environmental and efficiency concerns, manufacturers have begun replacing large V8s with turbocharged V6s or hybrid systems. Ford’s efficiency V6 in the F-150, for example, offers similar power with better fuel economy.
7.2 Hybrid V8s and Electrification
Some manufacturers are integrating V8 engines with electric motors for enhanced performance and efficiency. For example, Ferrari and McLaren have used hybrid V8s in their hypercars, like the LaFerrari and P1.
7.3 Advanced Technology in V8s
Modern V8s use advanced tech like:
-
Cylinder deactivation: Shuts down half the cylinders during light load to improve economy.
-
Direct injection: Improves power and reduces emissions.
-
Variable valve timing: Enhances performance across a broad RPM range.
The Future of V8 Cars
8.1 Regulation Pressure
With countries like the UK and parts of the EU planning to ban internal combustion engines by 2035, the V8’s future is uncertain. Automakers are under pressure to meet CO2 targets, leading to the phase-out of larger engines.
8.2 Enthusiast Market and Collector Value
While mainstream production may decline, V8 cars are gaining value as collector’s items. Models like the Dodge Challenger Hellcat, C7 Corvette Z06, and Mercedes C63 AMG may soon be viewed as the last of a legendary breed.
8.3 Electric Performance vs. V8 Legacy
Electric vehicles (EVs) now challenge V8s in performance. Tesla’s Model S Plaid and the Rimac Nevera out-accelerate nearly all combustion-engine cars. However, for many, EVs still lack the soul and visceral thrill of a V8.
Notable Modern V8 Cars
9.1 Dodge Challenger Hellcat
With 707+ horsepower, the Hellcat is a modern muscle car that pushes V8 performance to the extreme.
9.2 Chevrolet Corvette C8
The C8’s mid-engine 6.2L V8 makes it a performance bargain, rivaling European supercars.
9.3 Mercedes-AMG GT
Combining German precision with V8 power, the AMG GT represents the luxury sports car ideal.
9.4 Ford Mustang GT
Still going strong, the Mustang continues the legacy of V8-powered American performance.
Conclusion
The V8 engine remains one of the most iconic and celebrated engineering feats in automotive history. Its unique combination of power, sound, and mechanical emotion has carved a permanent place in the hearts of drivers and collectors. From muscle cars to luxury sedans, and from racetracks to city streets, the V8 has proven its versatility and enduring appeal.
However, the road ahead is uncertain. As the automotive industry shifts toward electrification and sustainability, the traditional V8 may be relegated to history—or reborn in hybrid form. Regardless of its future, the legacy of the V8 is secure. It has not only moved cars but moved people—emotionally and culturally.
For enthusiasts, the V8 car is not just about transportation. It’s about freedom, identity, and the raw joy of driving. And for as long as they exist


Vấn đề bảo mật luôn được thương hiệu quan tâm và đặt lên hàng đầu. Hội viên khi tham gia sẽ không cần phải lo lắng về vấn đề thông tin cá nhân quan trọng bị rò rỉ hoặc xâm nhập trái phép từ bên ngoài. trang chủ 66b Đăng Nhập không chỉ thiết lập một loạt chính sách quan trọng mà còn cung cấp tính năng mã hóa bảo vệ đa lớp cùng hệ thống tường lửa thép đặc biệt.
Sản phẩm xanh chín tiếp theo nhất định không nên bỏ qua khi cùng 66b ios đăng nhập vào đó chính là xổ số lô đề trực tuyến. Ngoài phiên bản truyền thống quen thuộc, sảnh chơi này còn đưa tới nhiều hình thức mới lạ khác để anh em tha hồ trải nghiệm, có thể kể đến như lô đề, keno, quay số,…..Mỗi tựa game sẽ có cách chơi khác nhau, nhưng đừng lo vì tất cả đều có hướng dẫn chi tiết cho người chơi trước khi chinh phục.
Những sản phẩm cá cược thể thao luôn được thiết kế với 4 phong cách khác nhau như OW – Sự đa dạng, TP – Tượng trưng cho hiện đại, SB – Sự truyền thống, KS – Trải nghiệm. Bảng tỷ lệ kèo 888slot link alternatif chính thức luôn cập nhật mới mỗi ngày để tiện cho anh em chủ động tham khảo, tỷ lệ thưởng luôn hấp dẫn, tối ưu cơ hội chiến thắng cho thành viên tham gia. TONY12-19
Just downloaded the jjwinapk app. So far, so good – pretty easy to navigate. Gonna give it a proper run tonight. Hoping for some wins! Get the app, guys jjwinapk!
Chỉ trong 5 năm ngắn ngủi, 888slot đã ghi nhận hơn 5,2 triệu người dùng đăng ký trên toàn hệ thống, với mức tăng trưởng trung bình 48% mỗi quý – một con số ấn tượng mà không phải tân binh nào cũng làm được. TONY01-09
Thông tin cá nhân của người chơi được bảo mật với bất kỳ bên thứ ba nào khi không có sự đồng ý của bạn. 888slot Mọi dữ liệu người dùng cung cấp khi đăng ký tài khoản hoặc thực hiện giao dịch đều được lưu trữ an toàn chỉ được sử dụng cho mục đích duy nhất là phục vụ khách hàng tốt hơn. TONY01-09
Nhóm 2: Tập trung vào Slot Game & Casino (20 đoạn) TONY01-30H
Slot tại đăng ký 66b có biểu tượng “?” giải thích luật chơi ngay trong game – bạn không cần thoát ra ngoài để tra cứu, tiết kiệm thời gian và chơi liền mạch. TONY02-03